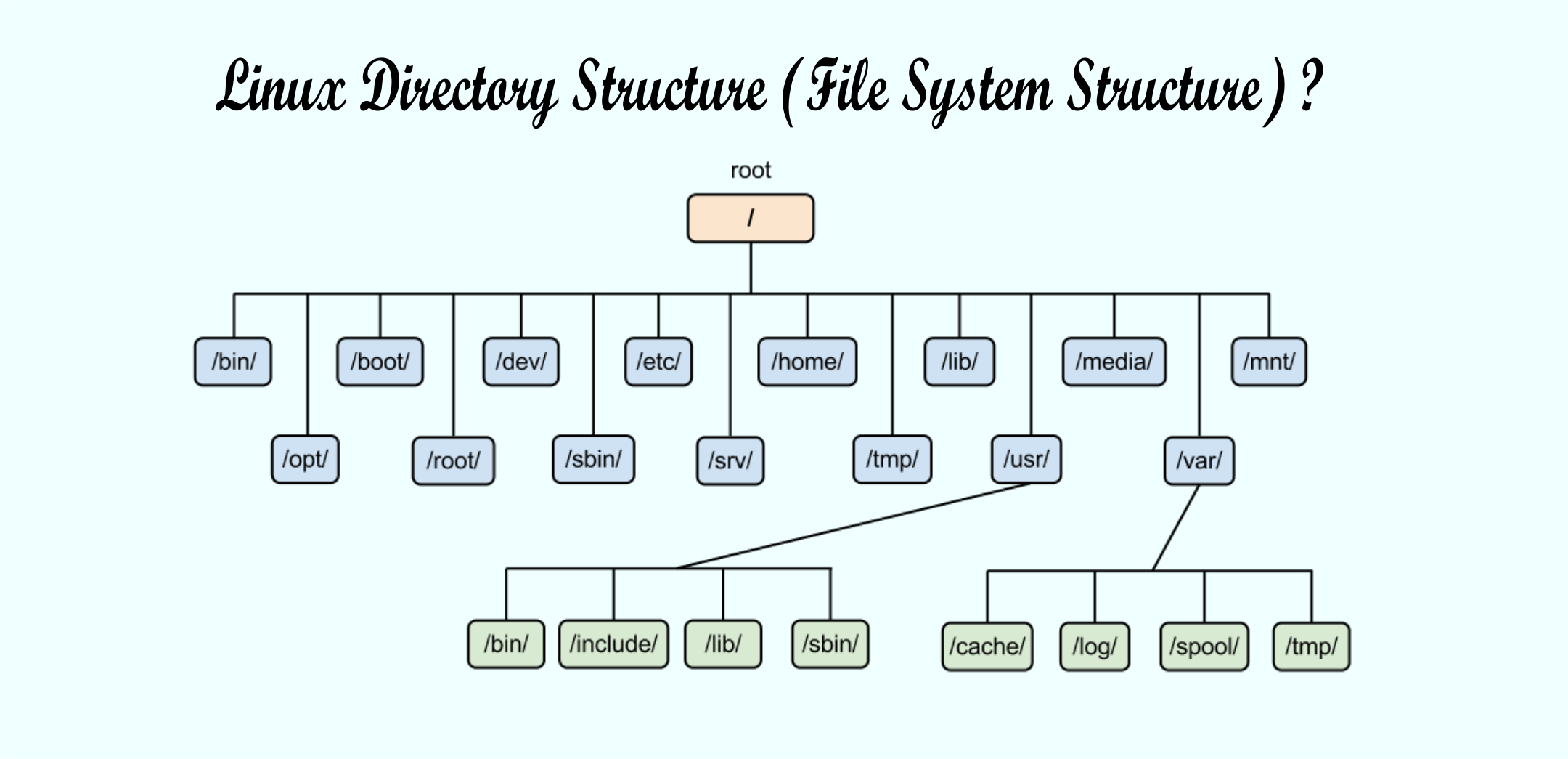
Have you wondered why certain programs are located under /bin, or /sbin, or /usr/bin, or /usr/sbin (File System Structure)
Example, less command is located under /usr/bin directory. Why not /bin, or /sbin, or /usr/sbin ?
In this article, let us review the Linux (File System Structure) and understand the meaning of individual high-level directories.
What is the difference between all these directories(File System Structure)?

1. / – Root
Every file and directory that starts from this directory only.
Under this directory, only the root user has to write privileges.
Make note that /root is root user’s home directory, which is not the same as /.
2. /bin – User Binaries
This Folder Contains only the binary executables.
Basic and Common Linux commands that we are using in single-user-mode are located in this directory.
The Normal users are used to run commands that are all located under this directory.
Example, they are ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
3. /sbin – System Binaries
Just like user binaries, /sbin also contains binary executables.
In this Directory commands that are only used by the System administrators for system maintenance purpose.
Example iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon
4. /etc – Configuration Files
The configuration files that are required by all programs located under this directory.
It Will also contains startup and shutdown shell scripts that are used to start/stop individual programs.
Example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf
5. /dev – Device Files
Contains device files.
These include terminal devices, USB, or any device attached to the system.
Example: /dev/tty1, /dev/usbmon0
6. /proc – Process Information
This Folder Contains information about system process.
This is a pseudo filesystem contains information about the running process. Example, The process with that particular pid information is located under /proc/pid.
This is a virtual filesystem with text information about system resources. Example: /proc/uptime
7. /var – Variable Files
var stands for variable files.
Content of the files that are expected to grow can be found under this directory.
This includes — system log files (/var/log); packages and DB files (/var/lib); emails located in (/var/mail); print queues located in (/var/spool); lock files under (/var/lock); temp files needed across reboots (/var/tmp);
8. /tmp – Temporary Files
Directory that contains temporary files created by system and users.
Files under this directory are deleted if the system is rebooted.
9. /usr – User Programs
It Contains binaries, libraries, documentation, and source-code for second level programs.
/usr/bin contains binary files for user programs. if it is not under user binary /bin means please find it in /usr/bin because in some distros version it may vary.
/usr/sbin contains binary files for super users. if it is not under system binary under /sbin, look under /usr/sbin. Example: cron, sshd, useradd, userdel
/usr/lib contains libraries for /usr/bin and /usr/sbin
/usr/local contains users programs that you install from source. Example, when you install apache from source, it goes under /usr/local/apache2
10. /home – Home Directories
Home directories for all users to store their personal files.
Example: /home/tharun
11. /boot – Boot Loader Files
Contains boot loader related files.
Kernel initrd, vmlinux, grub files are located under /boot
Example: initrd.img-2.6.32-24-generic, vmlinuz-2.6.32-24-generic
12. /lib – System Libraries
Contains library files that support the binaries located under the /bin and /sbin
Library filenames are ld* or lib*.so.*
13. /opt – Optional add-on Applications
opt stands for optional.
Contains add-on applications from individual vendors.
add-on applications should be installed /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
14. /mnt – Mount Directory
Temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount filesystems.
15. /media – Removable Media Devices
Temporary mount directory for removable devices.
For examples, /media/cdrom for CD-ROM; /media/floppy for floppy drives; /media/cdrecorder for CD writer
16. /srv – Service Data
The srv is stands for service data.
It Contains server specific services that are related to data.